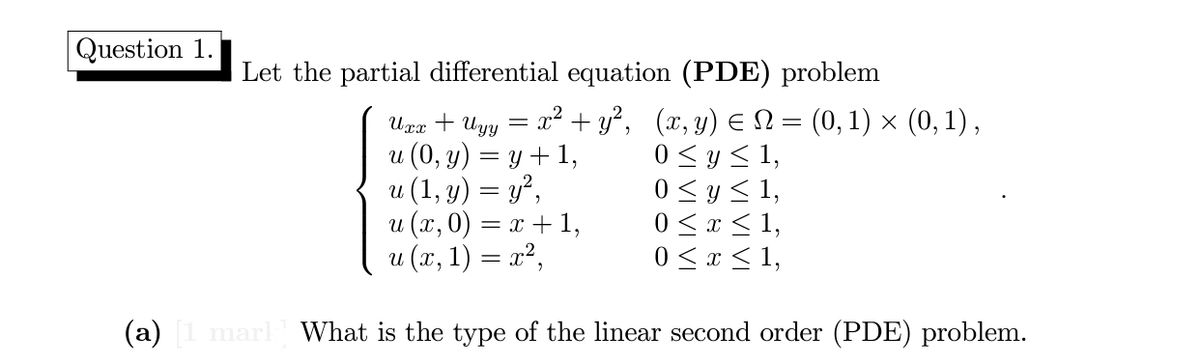
[最も人気のある!] f(x y z x^2 y^2 z^2)=0 pde 210122-F x y z x 2 y 2 z 2 0 pde
0 04 08 x 0 02 04 06 y 08 1 0 02 04 06 08 1 z 0 02 04 08 1 x 0 02 04 06 08 1 y Figure 8 Q4 Left The solid E;Plot the ellipsoid f (x, y, z) = x^2 2y^2 3z^2 = 1 together with the tangent plane at the point (1, 0, 0) Using MATLAB code Who are the experts?Answer \begin{align}x^2p^2y^2q^2=z^2\end{align}\tag*{} First thought Maybe we can transform it somehow into one of those f(p,q)=0 form by making some substitution Let's think To begin with, we can rewrite it this way \begin{align}\left(\dfrac{x}{z}\dfrac{\partial z}{\partial x}\right)^2

Solve The Equation X 2p 2 Y 2q 2 Z 2 Mathematics 2 Question Answer Collection
F x y z x 2 y 2 z 2 0 pde
F x y z x 2 y 2 z 2 0 pde-3im mostly having trouble converting to spherical for the ranges (x^2y^2)^(1/2)< Z < (18x^2y^2)^(1/2) 0 < X < (9y^2)^(1/2) 0The derivatives respect to x and y are z_x = f'(u)u_x = f'(u)(2x y) z_y = f'(u)u_y = f'(u)x Then f'(u) = z_x/(2xy) = z_y/x ,The PDE is z_x/(2xy) z_y/x =0 To eliminate the function f(x^2 xy) you can take u = x^2 xy



Solved Consider The Vector Function F X Y Z E X Sin Y Z Y E X Cos Y Xz Y 2 X Y 1 Z A
Example 2 Let F(x,y,z )=(x2z √ x3x22 , xy, xy √ z3z22) Compute R c F ·ds, where c is the circle x2 z2 = 1 , y = 0 , oriented in the10 Solve (D DD D z2 2− =2 ' ' 0 Soln Auxiliary Equation is m m2 − =2 1 0 ie, ( 1) 0m− =2 m= 1,1 y f y x xf y x= 1 2( ) ( ) 11 Find the complete solution of the PDE p q pq2 2 − =4 0 Soln Given p q pq2 2 − =4 0(1) Assume z ax by ca= (2) be the solution of (1) Differentiating (1) partially with respect to 'x' and 'y' we getRead the following information and answer the three items that follow Let f ( x) = x 2 2 x − 5 and g ( x) = 5 x 3 0 If h ( x) = 5 f ( x) − x g ( x), then what is the derivative of h ( x) ?
352 Chapter 14 Partial Differentiation k;Find the minimum of the function f(x;y;z) = x2 y2 z2 subject to the condition x2y 3z = 4 Solution Let's deflne g(x;y;F(x,y,z,p,q) = 0 (2) The equations of the type (2) arise in many applications in geometry and physics For instance, consider the following geometrical problem EXAMPLE 1 Find all functions z(x,y) such that the tangent plane to the graph z= z(x,y) at any arbitrary point (x0,y0,z(x0,y0)) passes through the origin characterized by the PDE xzx
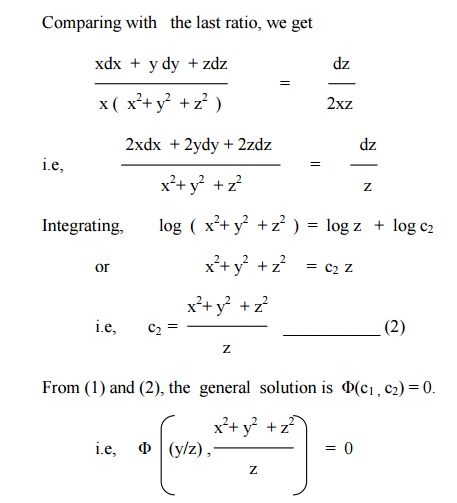
Eg x2p y2q = z is a linear in z and of first order Further, a pde is said to be quasilinear if degree of highest order derivative is one, no product of partial derivatives are present eg z – z xx (z y)2 = 0 is a quasilinear 2nd order 112 FORMATION OF PARTIAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONSNow differentiating the last result with respect to zz z we obtain ∂f(x,y,z)∂z=xy22x2zh′(z)\\frac{\\partial f(x, y,z)}{\\partial z}=xy^{2}2x^{2}zhSometimes, it is possible to have non –linear partial differential equations of the first order which do not belong to any of the four standard forms discussed earlier By changing the variables suitably, we will reduce them into any one of the four standard forms Type (i) Equations of the form F(x m p, y n q) = 0 (or) F (z, x m p, y n q) = 0




Let W X Y Z 1 Sqrt X 2 Y 2 Z 2 X Y Z 0 0 0 Show That Del 2 W Delx 2 Del 2 W Dely 2 Del 2 W Delz 2 0




Math 467 Partial Differential Equations Exercises Millersville
1;0) with values f(x;y;z) = 5 and 1 Case 2 If z ̸= 0, the third equation gives = 1 Then the second equation gives 2y = 2y or y = 4 Then pluggingIn general this is called a level set;Easy View solution > Difference between the greatest and the least values of the function f ( x) = x ( l n x − 2) on 1, e 2 is




Ordinary Differential Equations The Decision Of Three Methods Of The Solutions Dx P Dy Q Dz R Mathematics Stack Exchange



What Is The Form A Pde By Eliminating The Arbitrary Function Phi From Phi X 2 Y 2 Z 2 Z 2 2xy 0 Can Someone Solve It Quora
Solve your math problems using our free math solver with stepbystep solutions Our math solver supports basic math, prealgebra, algebra, trigonometry, calculus and more3 Find the PDE of all spheres whose centre lie on the (i) z axis (ii) xaxis 4 Form the partial differential equations by eliminating the arbitrary functions in the following cases (i) z = f (x y) (ii) z = f (x2 –y2) (iii) z = f (x2 y2 z2) (iv) f(xyz, x y z) = 0 (v) F (xy z2, x y z) = 0Stack Exchange Network Stack Exchange network consists of 180 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow , the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build



Level Surfaces



2
Right The image of E on xyplane 5 Find the volume remaining in a sphere of radius a after a hole of radius b is drilled through the centre1 BASICCONCEPTS 2 2 Verify that for all pairs of differential functions f and g of one variable, u(x,y) = f(x)g(y) is a solution of the PDE uuxy = uxuy Solution First, compute ux, uy and uxy ux = g(y)f′(x) uy = f(x)g′(y) uxy = f′(x)g′(y) Substituting into the PDE, we have The gradient is = The gradient is a vector gradf=((delf)/(delx), (delf)/(dely), (delf)/(delz)) f(x,y,z)=3x^2yy^3z^2 (delf)/(delx)=6xy (delf)/(dely



2



Chapter 1 Vector Analysis
F(x,y ∆y,z)−f(x,y,z) ∆y (2) ∂f ∂z = lim ∆z→0 f(x,y,z ∆z)−f(x,y,z) ∆z (3) These formulae are direct generalisations of the well known definition of the derivative of a function f(x) of one variable x df dx = lim ∆x→0 f(x∆x)−f(x) ∆x (4) Example Let f(x,y,z) =Evaluate Z 2 0 x y2 1 dy Solution Since we are integrating with respect to y, the letter x in the integrand is treated as a constant We have Z0 $ written 60 years ago by teamques10 ★



1




Partial Differential Equation Notes
You need to evaluate all second degree terms, 3x^2−2xy3y^2 In this case it will work, as the coefficients of x^2 and y^2 are equal, so that the terms 2\cos\theta\sin\theta XY will cancelX^ {2}y^ {2}z^ {2}\left (yz\right)xyz=0 x 2 y 2 z 2 ( − y − z) x − y z = 0 All equations of the form ax^ {2}bxc=0 can be solved using the quadratic formula \frac {b±\sqrt {b^ {2}4ac}} {2a} The quadratic formula gives two solutions, one when ±Extended Keyboard Examples Upload Random Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, history, geography, engineering, mathematics, linguistics, sports, finance, music
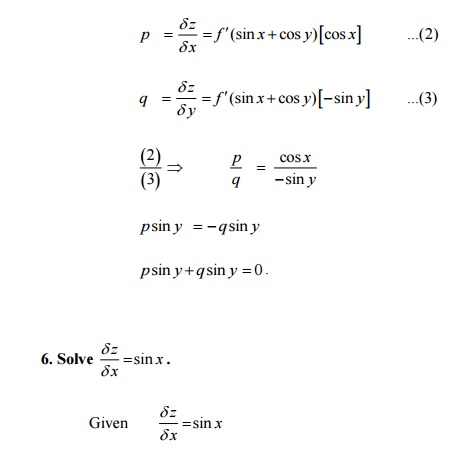



Important Questions And Answers Partial Differential Equations




Mte 08 Assignment 1
Extended Keyboard Examples Upload Random Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, history, geography, engineering, mathematics, linguistics, sports, finance, musicForm a PDE by eliminating the arbitrary function (i) $\displaystyle F(xyz^2,xyz)=0 $ (ii) $\displaystyle F(xyz,x^2y^2z^2)=0 $ How do I proceed for any of these?For three variables, a level set is typically a surface, called a level surface EXAMPLE 1415 Suppose the temperature at (x,y,z) is T(x,y,z) = e−(x2y2z2) This function has a maximum value of 1 at the origin, and tends to 0 in all directions




Linear First Order Pdes




18mat21 Module 3 Lct 04 Pde By Eliminating Function 1 Z Y 2 2f 1 X Logy 2 Xyz F X Y Z Youtube
1 f(x,y) C C 1 2 x y z f (0,0) = f (0,0) = 0 x y Remark This is a bad property for a differentiable function Partial derivatives and continuity Remark Here is a discontinuous function at (0,0) having partial derivatives at (0,0) Example (a) Show that f is not continuous at (0,0), wherePlot z=x^2y^2 Natural Language;From z =(xy)f(x^2 y^2) means that the solution of the partial differential equation is given by an arbitrary function F( z/(xy) , x^2y^2 )=0 of class C2 with respect to variables x , y Take u = z/(xy) , v = x^2 y^2 , so obtain F( u,v ) =0Differentiating respect to x and y and taking p = z_x ,




Tpde 3 Pdf Partial Differential Equation Mathematical Objects



How To Complete The Partial Differential Equation By Eliminating The Arbitrary Function From The Relation F X Y Z Xy 0 Quora
1(x) f 2(y)Answer @z @x = y @2z @y@x 2 Form the partial di erential equation by eliminating the f and ˚from z = f(y) ˚(x y z) Answer r(1 q) = s(1 p) 3 Form a partial di erential equation from the relation by eliminating the arbitrary functions f 1 and f 2 from z = f 1(x 2y) f 2(x 2y) Answer 4@2z @x 2 = @2z @y 4Textbook Solutions Expert Tutors Earn Main Menu;Plot f(x,y,z)=x^2y^2z^2 Natural Language;



What Is The Integral Surface Of X Y 2 Z P Y X 2 Z Q X 2 Y 2 Z Through The Straight Through The X Y 0 Z 1 Quora
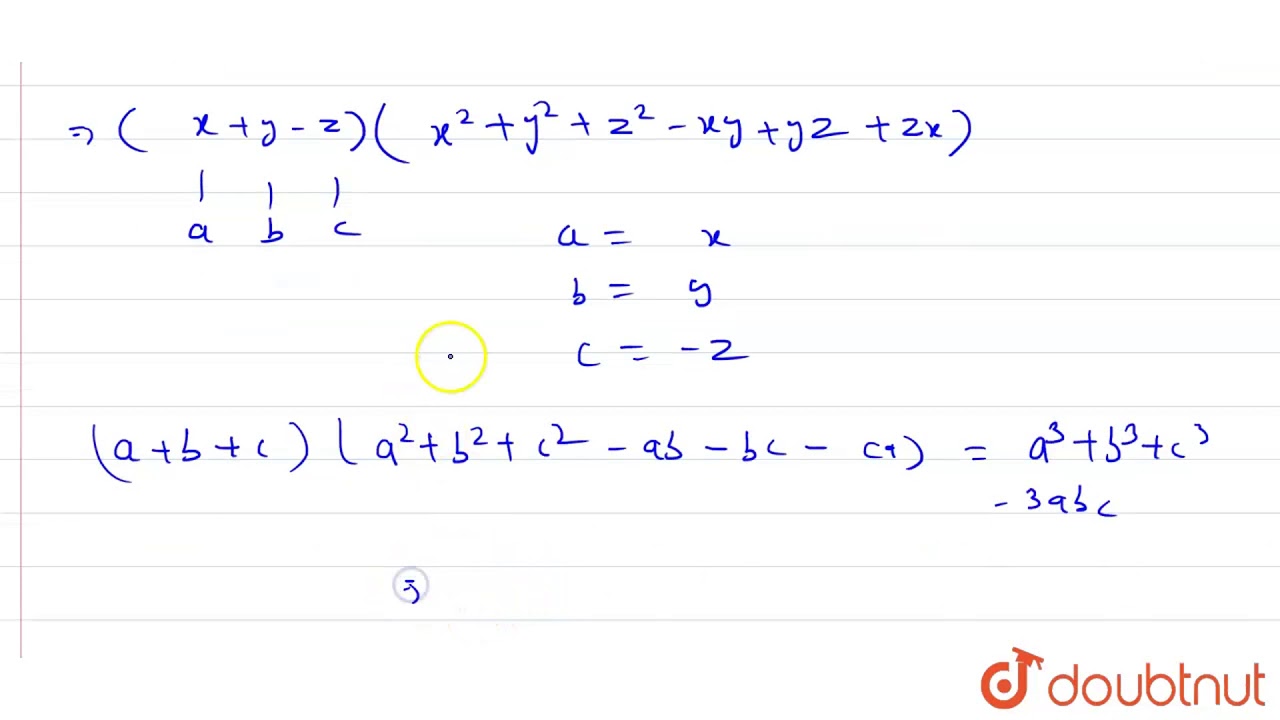



Find The Product X Y Z X 2 Y 2 Z 2 Xy Yz Zx Youtube
Extended Keyboard Examples Upload Random Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, history, geography, engineering, mathematics, linguistics, sports, finance, musicF(x,y,z) x^2y^2z^2here are the intervals(x^2y^2)^(1/2)<Solve your math problems using our free math solver with stepbystep solutions Our math solver supports basic math, prealgebra, algebra, trigonometry, calculus and more




Partial Differential Equations




Solve The Equation X 2p 2 Y 2q 2 Z 2 Mathematics 2 Question Answer Collection
30k • modified 22 years ago engineering mathematics ADD COMMENT FOLLOW SHARE EDIT 1Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high clc;clear all;format compact x=12;For f(x,y,z,a,b) = 0 differentiating wrto x,y partially and eliminating constants a,b we get a PDE Example 1 From the equation x2 y2 z2 = 1 form a PDE by eliminating arbitrary constant Solution z2 = 1 x2 y2 Differentiating wrto x,y partially respectively we get y y z x d z x z 2z 2 2 2 w w w w p = = x/z and q= = y/z z = x/p = y/ q qx = py is required PDE




Z F X Y Z Find Solution Of Given Partial Differential Equation Brainly In




Solved Form The Pde Of The Following By Eliminating Chegg Com
F(x,y,z,zx,zy) = 0 This is a PDE for the unknown function of two independent variables Exercise 21 Let f(x,y,a,b) = (x−a)2(y−b)2 Get a PDE by eliminating the parameters Also U(t0) = 0 in view of (27) as z = u(x,y) is an integral surface Hence by uniqueness of solutions of Initial value problems to ODEs, we conclude that3 (Exercise ) Find the minimum/maximum of f(x;y;z) = x2 y2 z2 subject to x y = 1 and y2 z2 = 1 Solution The gradient equation gives 2x = ;2y = 2 y;2z = 2 z Case 1 If z = 0, y2 z2 = 1 implies y = 1 and from x y = 1 we get the points (2;1;0) and (0;If $ u=f(xy,yz,zx) , $ then show that $ \dfrac{\partial u}{\partial x} \dfrac{\partial u}{\partial y} \dfrac{\partial u}{\partial z} \;=\;




Unit V Pde Converted Pdf Unit V Partial Differential Equations U27a2 Formation Of Partial Differential Equations By Elimination Of Arbitrary Constants Course Hero



2
Solve your math problems using our free math solver with stepbystep solutions Our math solver supports basic math, prealgebra, algebra, trigonometry, calculus and moreX y 1 z = 0 (1)4 y = 4 11 (2) 11 2 z = 7 4 (3) 将第 (3) 等式两边 乘以2 除以11后,可以得到等式:Transcribed image text For a scalar field f(x, y, z) = x^2 2y^2 3/2 z^2, calculate the integral integral integral partial differential f/partial differential n dA where S is the closed surface consisting of the cylinder x^2 y^2 = a^2 (0 lessthanorequalto z lessthanorequalto b) and the circulardisk z = 0 and z = b (x^2 y^2 lessthanorequalto a^2)



2




Solutions To Practice Final Exam Pdf Free Download
This equation is of the form f 1 ( x, p) = f 2 ( y, q) Its solution is given by d z = p d x q d y, upon integrating this we get value of z From (I) − y q 2 z q − a = 0, solving the quadratic equation for q, we get q = − z ± z 2 − 4 a y − 2 y Taking the positive value only, q = − z z 2 − 4 a y − 2 yMeans the second derivative with respect to y holding x constant † @ 2z @x@y means difierentiate flrst with respect to y and then with respect to x The \mixed" partial derivative @ 2z @x@y is as important in applications as the others It is a general result that @2z @x@y = @2z @y@x ie you get the same answer whichever order theExtended Keyboard Examples Upload Random Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, history, geography, engineering, mathematics, linguistics, sports, finance, music




Ma2211 Unit 3 Pdf Equations Differential Calculus



2
F x y z z z z y 0 Standard Notation z x p z z y q z x y 2 2 2 2 z x r z z y t z from MECHANICAL 128 at G H Raisoni College of Engineering Study Resources Main Menu;The partial differential equation obtained by eliminating arbitrary function from \( \Large z=f(x^{2}y^{2})\) isF(x)=x^2 zero of polynomial kodekala2 kodekala2 2 minutes ago Math Secondary School F(x)=x^2 zero of polynomial kodekala2 is waiting for your help Add your answer and earn points New questions in Math give me an example of A'UB with solved venn diagram if alpha =ONLY GOODIES then find (zoskhrwynu)² beta



2
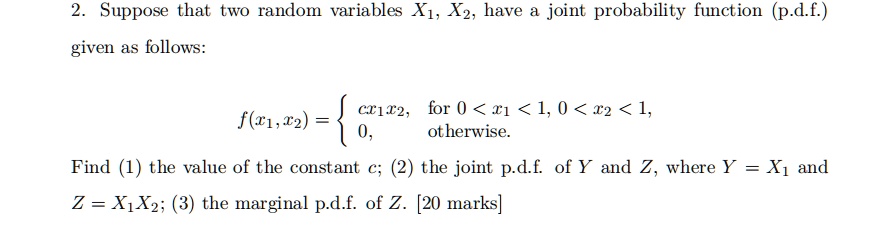



Solved Suppose That Two Random Variables X1 Xz Have Joint Probability Function P D E Given As Follows Ccit2 For 0 1 1 0 12 1 Otherwise F 1 T2 Find The Value
Extended Keyboard Examples Upload Random Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, history, geography, engineering, mathematics, linguistics, sports, finance, music x(−dx−dz)ydx2zdz=0 y−xx−2zdx=dz(7) Similarly xdyy(−dy−dz)2zdz=0 x−yy−2zdy=dz(8) From (7) and (8) we obtain dxx−2zy−x=dyy−2zx−y=dz dxx−2z=dy2z−y=dzy−x Finally we obtain the desired PDE for z(x,y) (x−2z)∂z∂x−(y−2z)∂z∂y=y−x The other implicit equation can be treated in a similar fashion




Partial Differential Equation Notes



2




One Dimentional Wave Eqn




Lagranges Pde Y 2 Z 2 X 2 P 2xyq 2zx Youtube




X 2p Y 2q X Y Zsolve The Following Pde Brainly In




Solved Find The General Solution Of The Following Partial Chegg Com
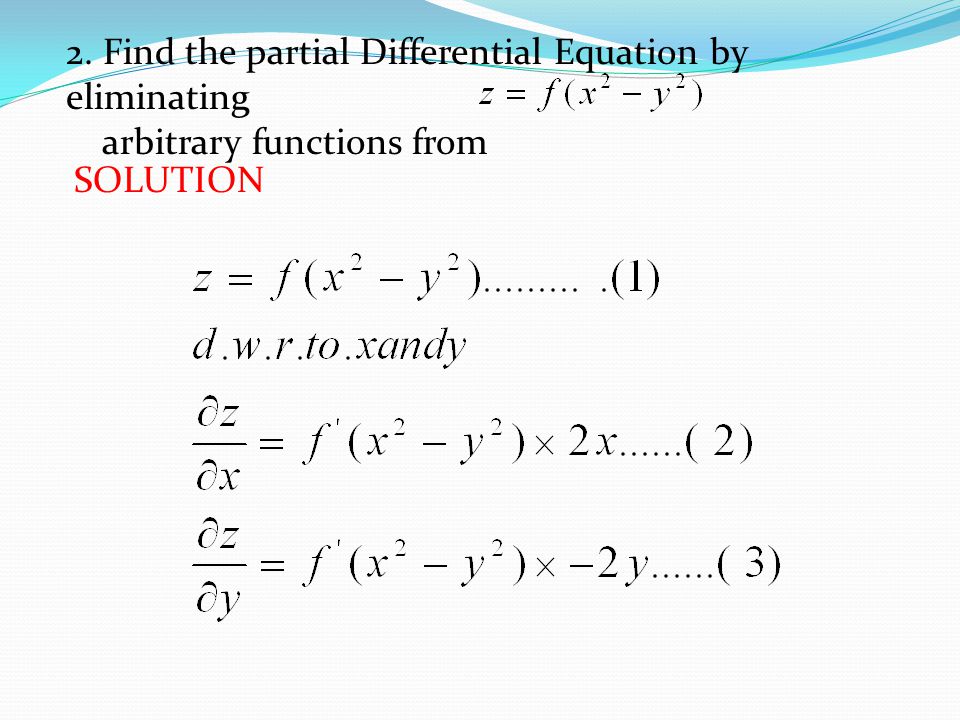



Partial Differential Equations Ppt Video Online Download




Ad Eng Math 6 8 15 Pages 1 244 Flip Pdf Download Fliphtml5



2




Partial Differential Equation Notes



2




Important Questions And Answers Partial Differential Equations




Partal Diff Equations




Chapter 1 Maths 3



Partial Differential Equation Notes




Lct 08 18mat21 Module 3 Formation Of Pde From F X 2 Y 2 Z 2 Lx My Nz 0 Youtube




2 Partial Differentiation



11 Partial Differential Equations



Solved Consider The Vector Function F X Y Z E X Sin Y Z Y E X Cos Y Xz Y 2 X Y 1 Z A




Ordinary Differential Equations The Decision Of Three Methods Of The Solutions Dx P Dy Q Dz R Mathematics Stack Exchange




Solved An Equation Which Involves Partial Derivatives Of A Chegg Com




Topic 4 Pde Note Topic 4 Solution Of Pfaffian Differential Equations In Three Variables When The Condition Of Integrability Is Satised Then We Use Course Hero




5 Partial Differential Equations Method Of Elimination Of Arbitrary Functions Studocu




Se Cse Pde Flipbook By Ghanshyam Dahirrao Fliphtml5



Form Pde From Z F 2x Y G 3x Y Math Homework Answers




Maths



Answered Let Thẻ Partial Differential Equation Bartleby



2



2




Important Questions And Answers Partial Differential Equations



Solved Solve The Pde Using Lagrange Methode Z Xp Yq Y 2 X 2 Course Hero




Solutions To Practice Final Exam Pdf Free Download




Ode Pde Laplace Transforms And Vector Analysis Unit
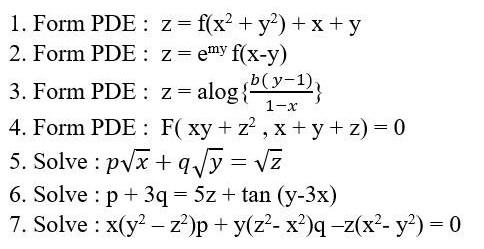



Solved 1 X 1 Form Pde Z F X Y2 X Y 2 Form Chegg Com



2



1




Pde 1 Pdf Partial Differential Equation Differential Equations



2




Chapter 9 Partial Differential Equations 13 Mathematical Methods For Physicists Seventh Edition Studocu




Solved Questi On L Characterize Each Of The Following Chegg Com



How To Complete The Partial Differential Equation By Eliminating The Arbitrary Function From The Relation F X Y Z Xy 0 Quora




Pdf On The Diophantine Equation X 2 C Y 2 D Z 4



Tp Lc Ehu Eus



Partial Differential Equations




X2 Y2 Z2 P 2xyq 2xz Brainly In
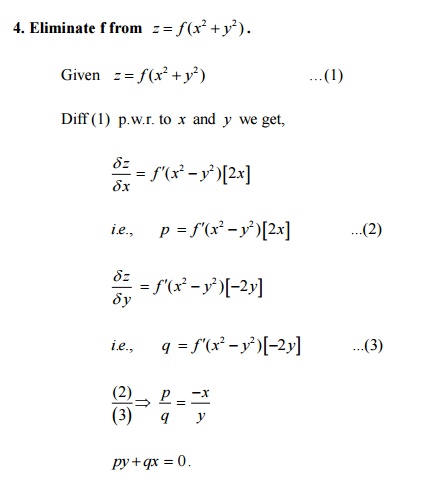



Important Questions And Answers Partial Differential Equations
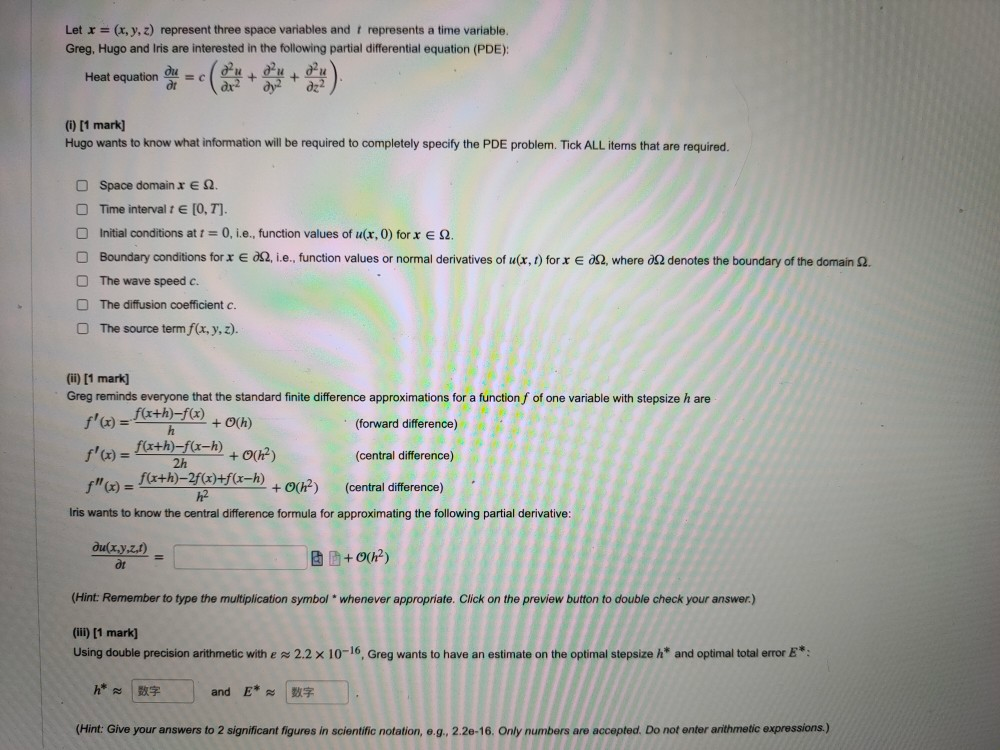



Solved Let X X Y Z Represent Three Space Variables And Chegg Com



What Is The Pde Associated With Z Yf X Xg Y Quora




Solved The Function F X Y Z Sx 4y Z Has An Absolute Maximum Value And Absolute Minimum Value Subject To The Constraint X Y Z 42 Use Lagrange Multipliers To Find These Values Find The Gradient




Solved Form The Partial Differential Equation By Eliminating The Arbitrary Function J Xyz Olx Y 2 Ii 2 6 6 Eliminate Arbitrary Constants A And H From The Following Relations




Solution Of First Order Linear Pde Pdf Partial Differential Equation Differential Calculus




Multiple Integrals H 2 Y Are Continuous Functions On C D And Let F X Y Be A Function Defined On R Then Pdf Free Download




Differential Equations Matha College Of Technology



2




One Dimentional Wave Eqn




Verifying Solutions To Differential Equations Video Khan Academy




Ordinary Differential Equations How Is Frac Dx Z X Y Frac Dy Z X Y Frac Dz X 2 Y 2 Equivalent To Frac Y Dx Xdy Zdz 0 Frac Xdx Ydy Zdz 0




Partial Derivatives Examples F X Y Z Z E Xyz Youtube



How To Use The Lagrange Method To Solve The Partial Differential Equation Defined By 4 U Sub X Minus 3u Sub Y Equal To Zero With Auxiliary Condition U 0 Y Y 3 Quora



How To Solve The Partial Differential Equation P 2 Q 2 Npq Quora




Sheet 5 Lagranges Equation Docx Lagrange S Method Of Solving The Quasi Linear Partial Differential Equation Of Order One Namely Pp Qq R Known As Course Hero



1




Chapter 1 Maths 3




Important Questions And Answers Partial Differential Equations




If U Log X 2 Y 2 Z 2 Verify 2u X Y 2u X Y




Solved Let X X Y Z Represent Three Space Variables And Chegg Com
コメント
コメントを投稿